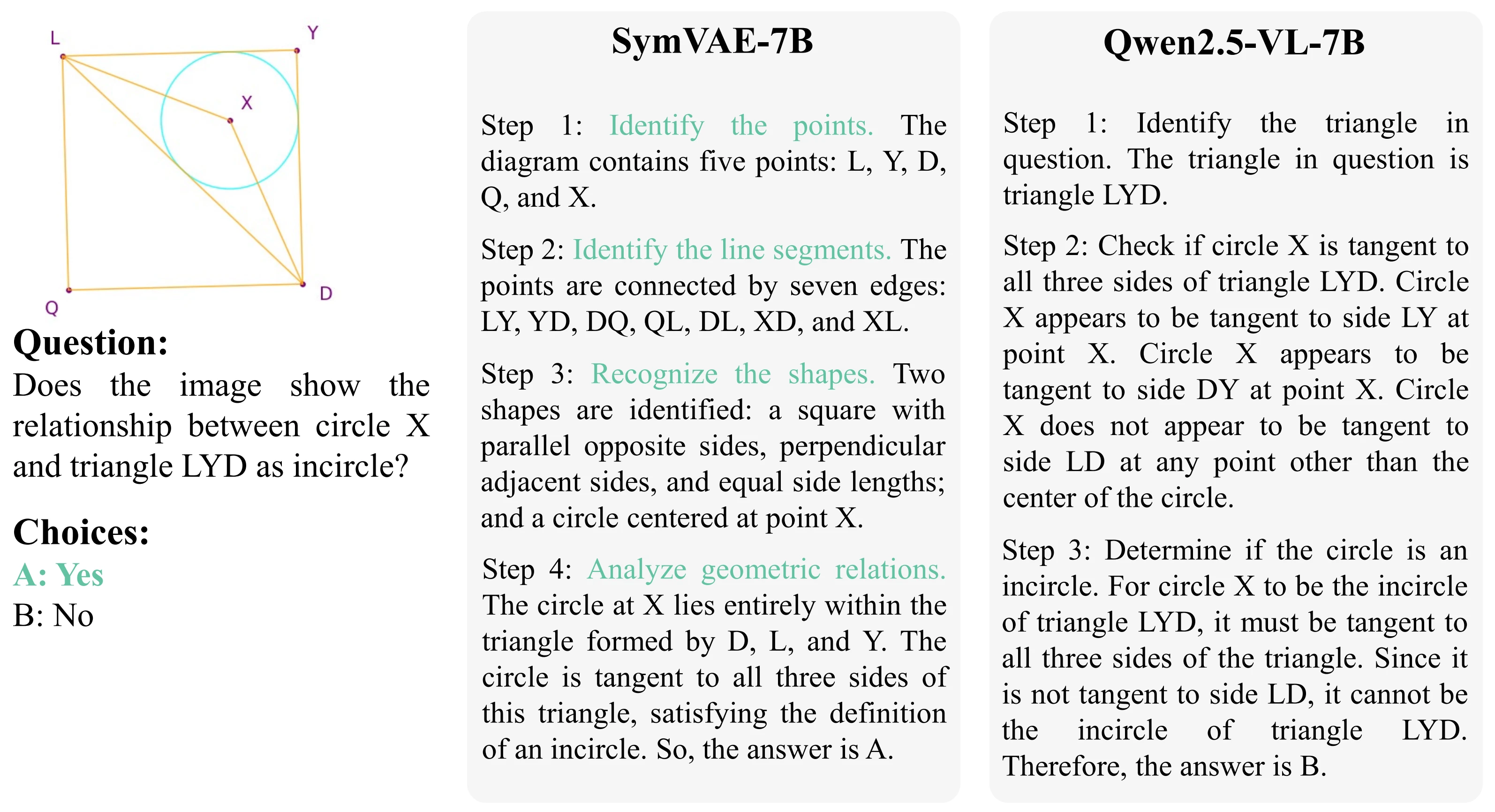
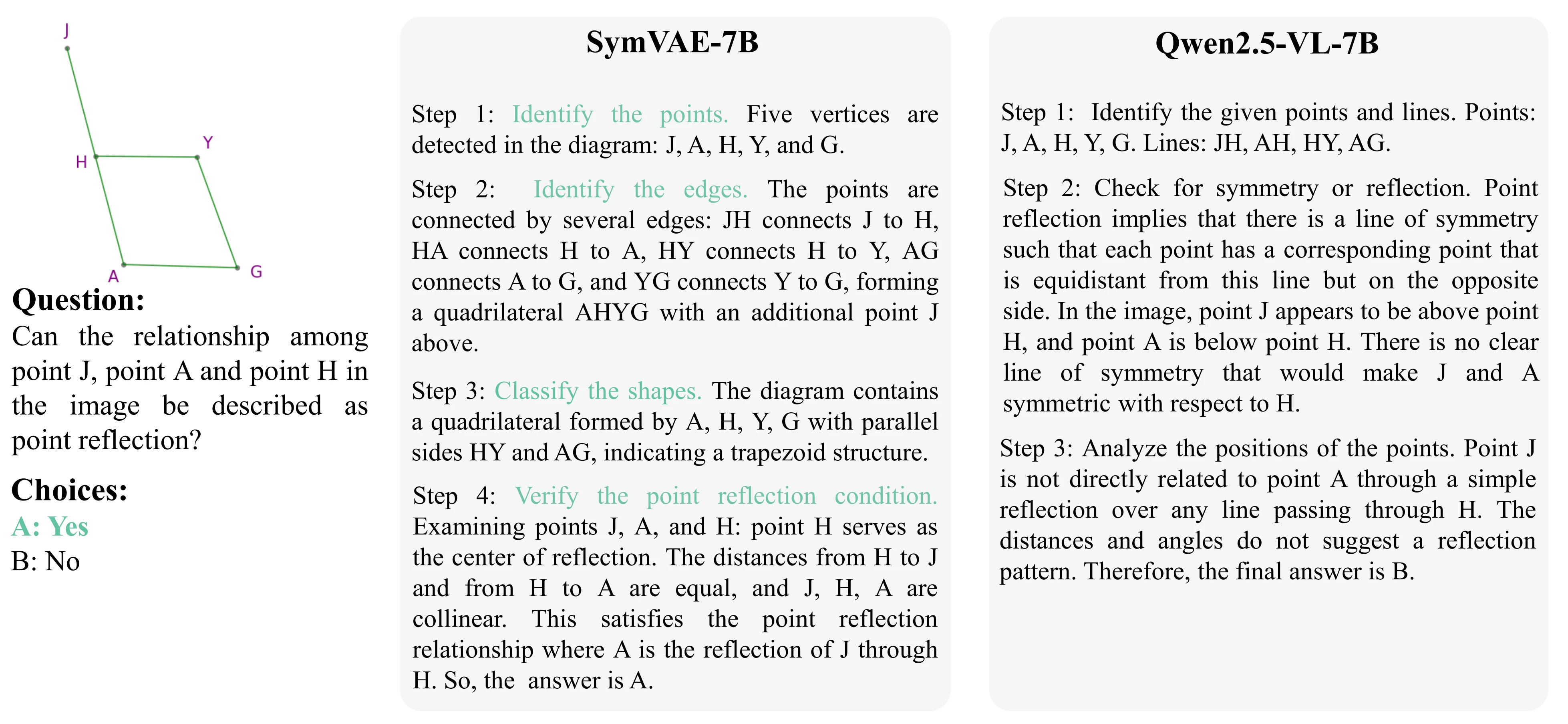
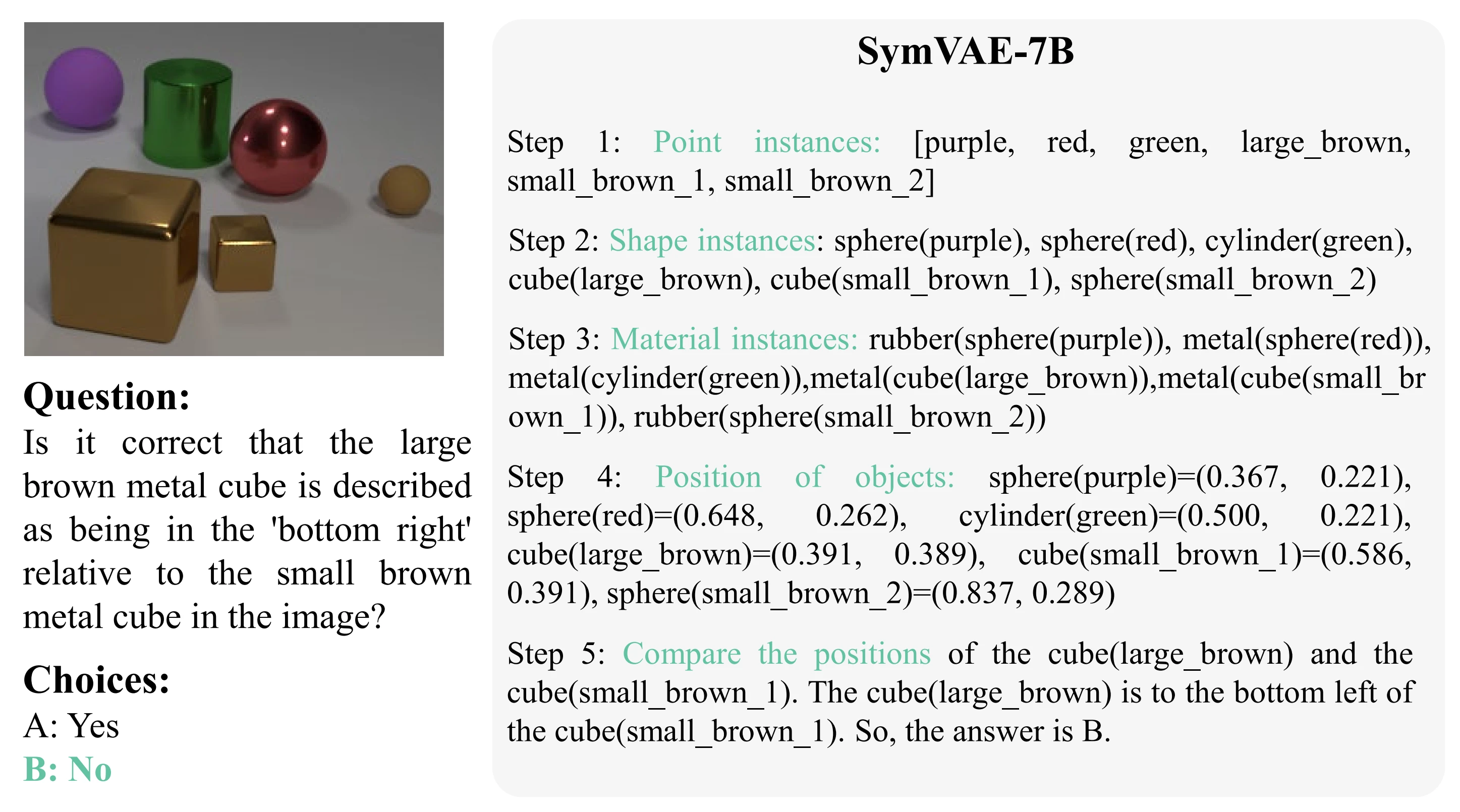
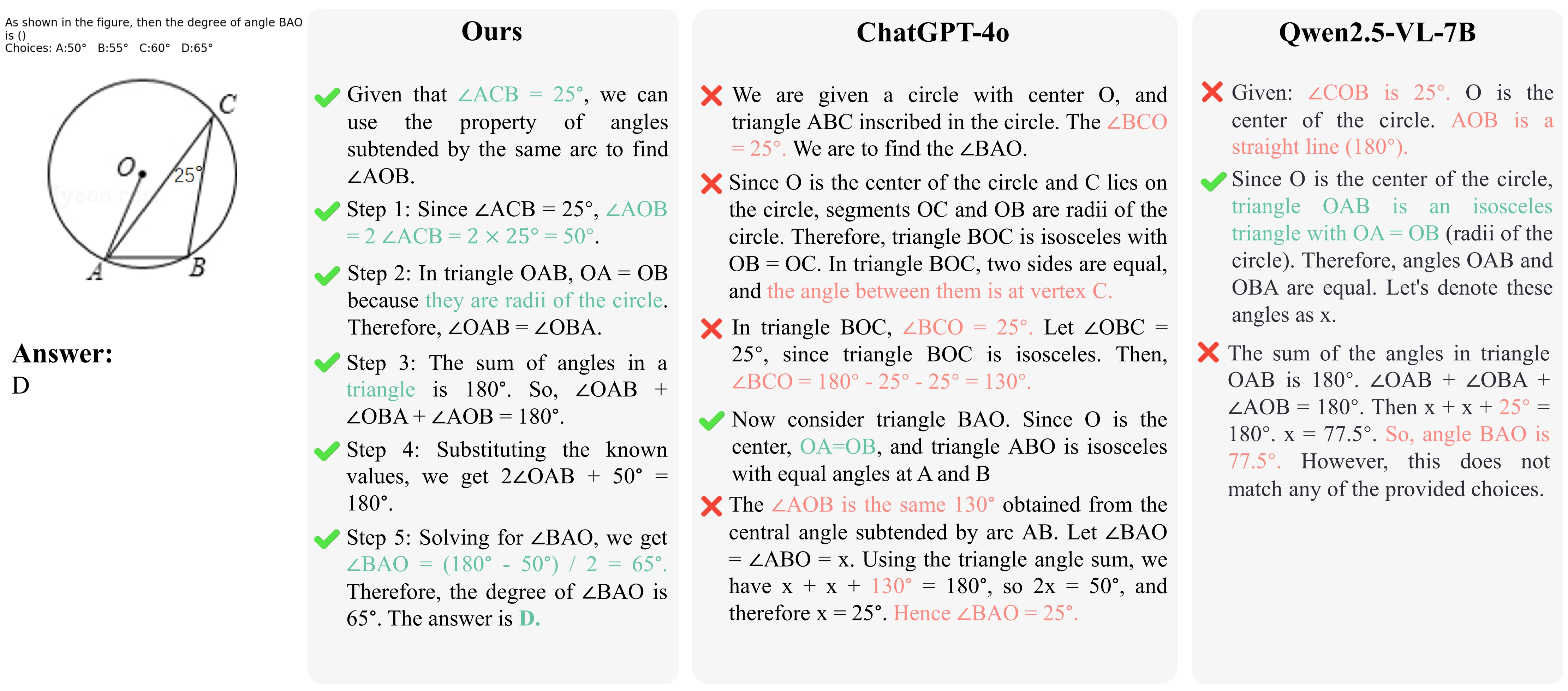
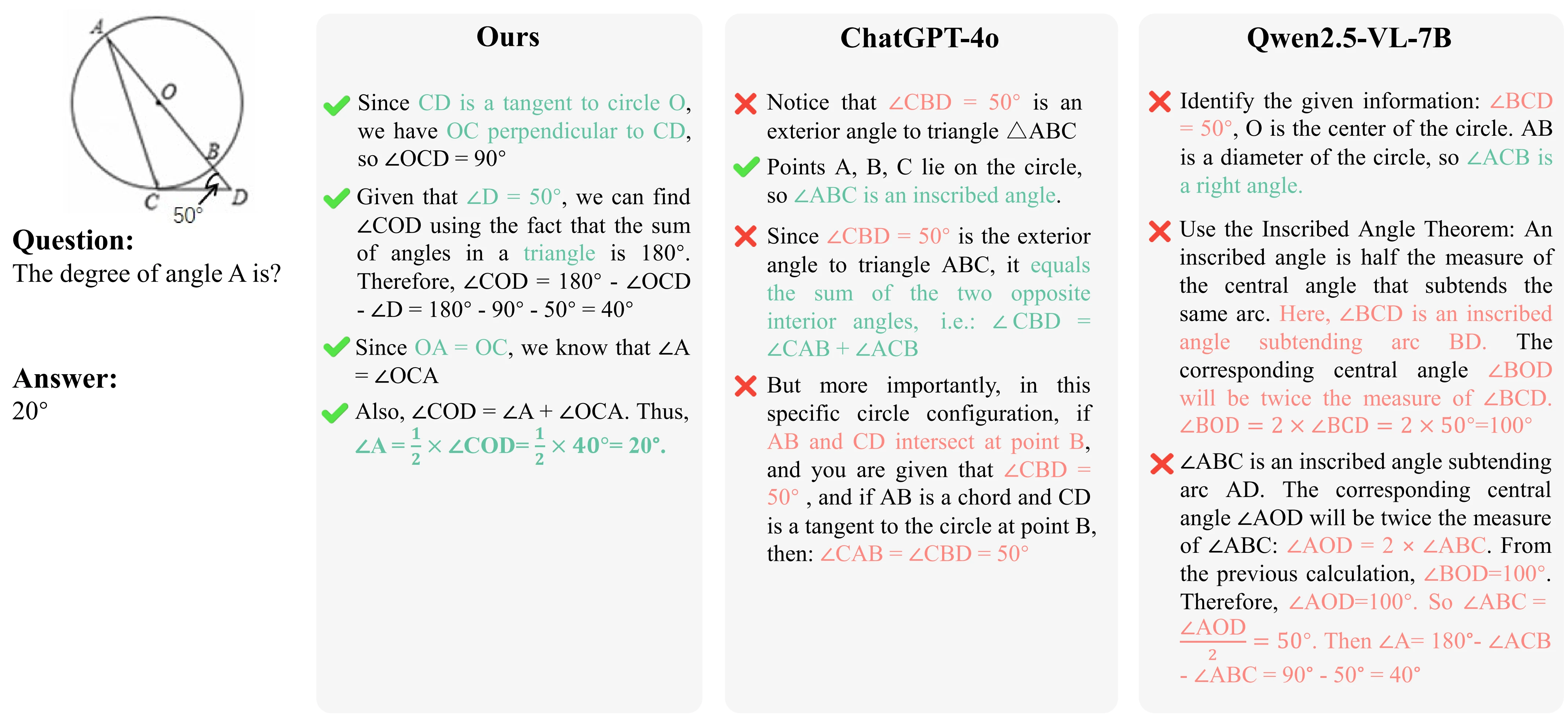
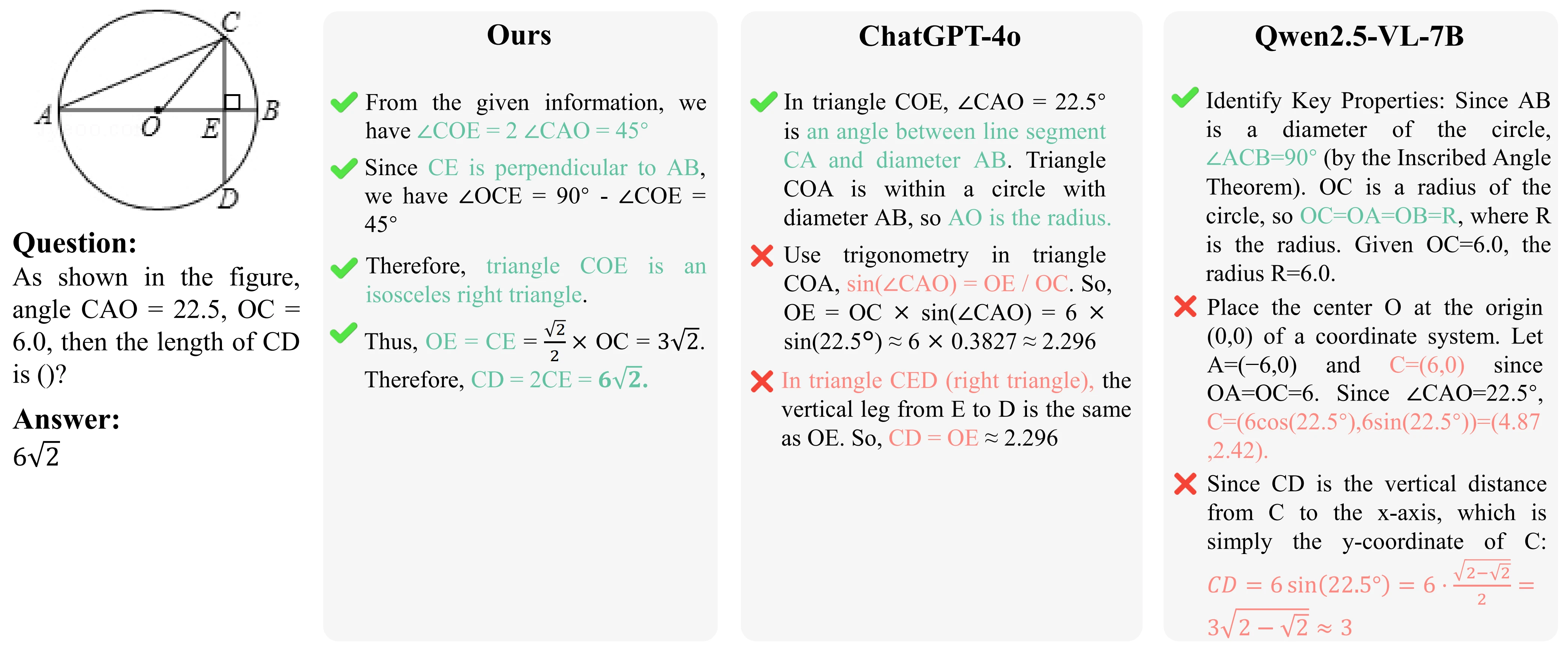
Method
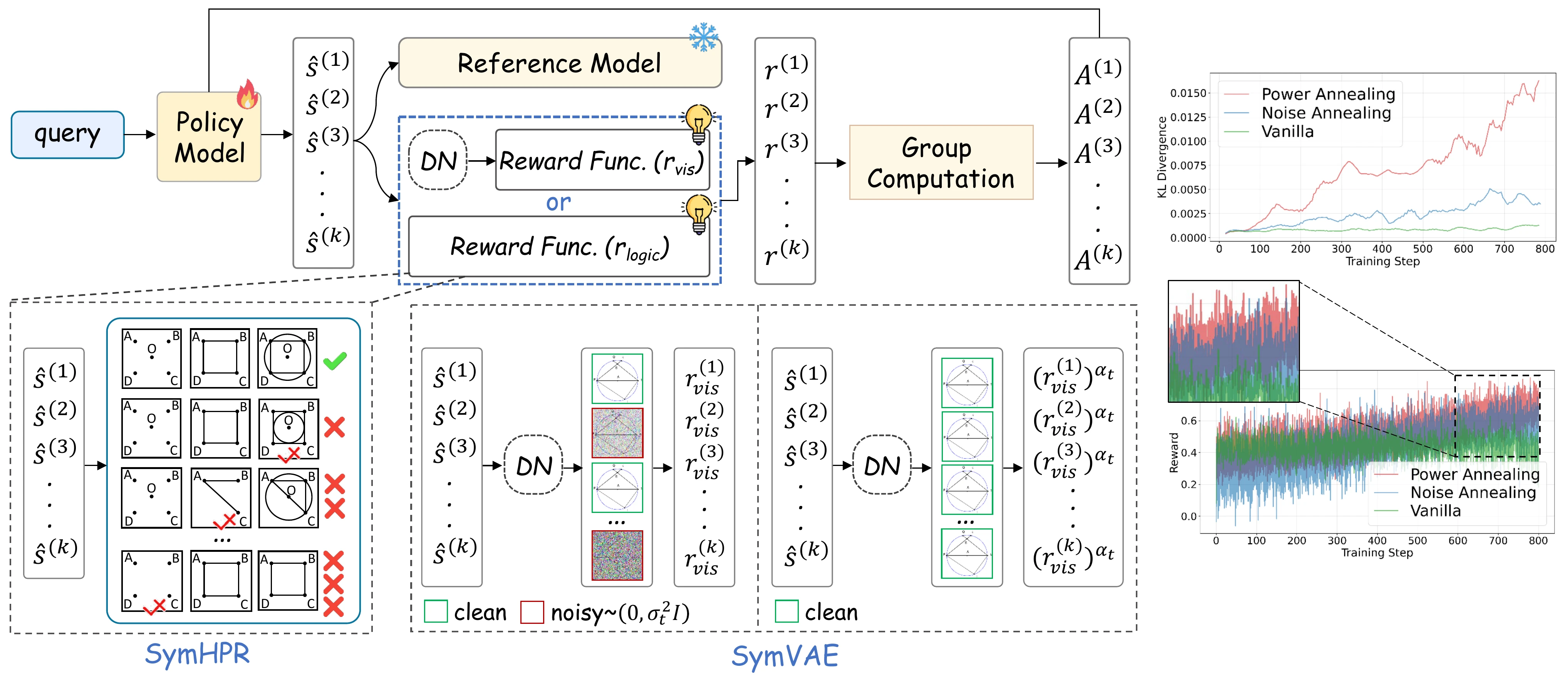
Key Innovations
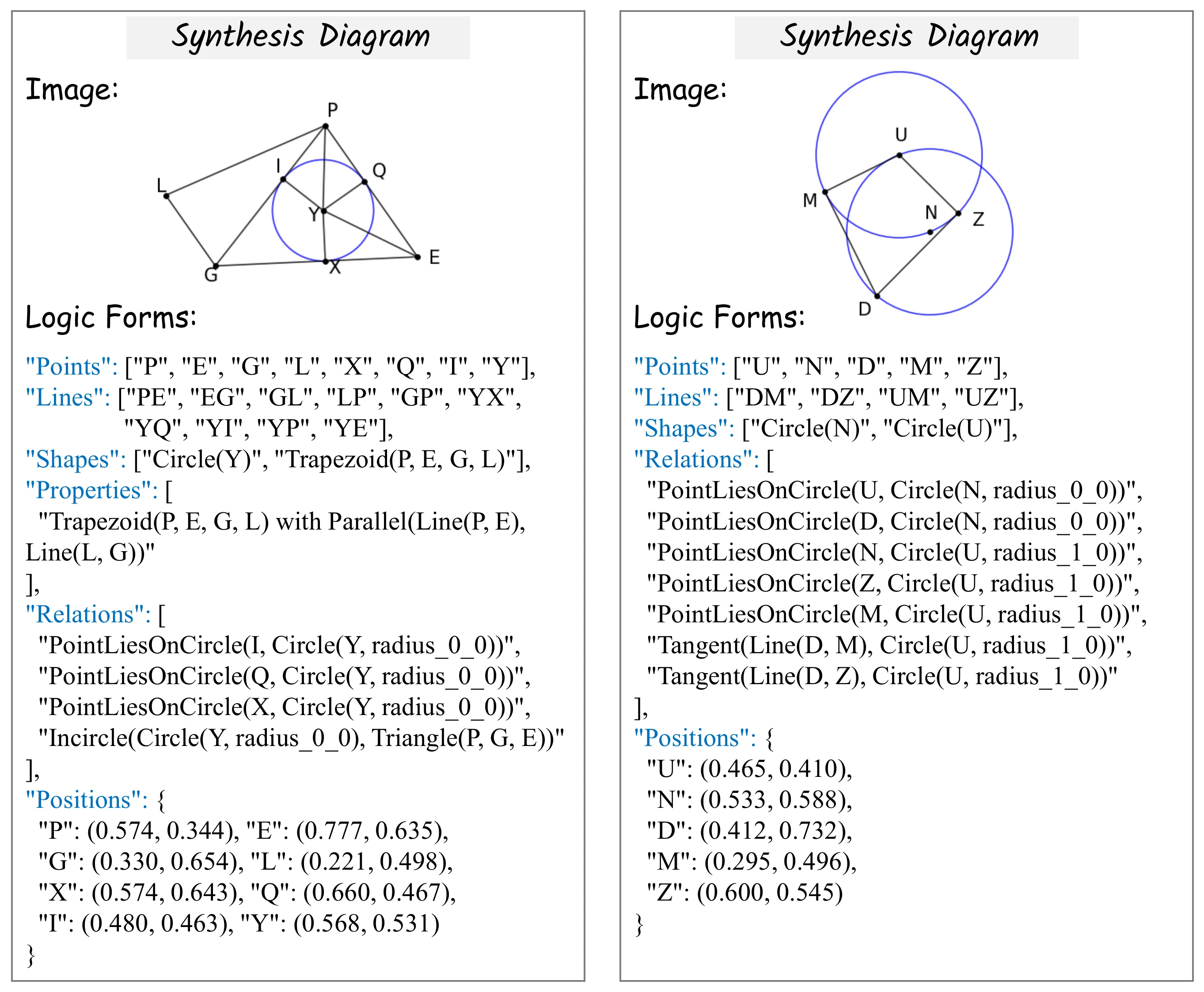
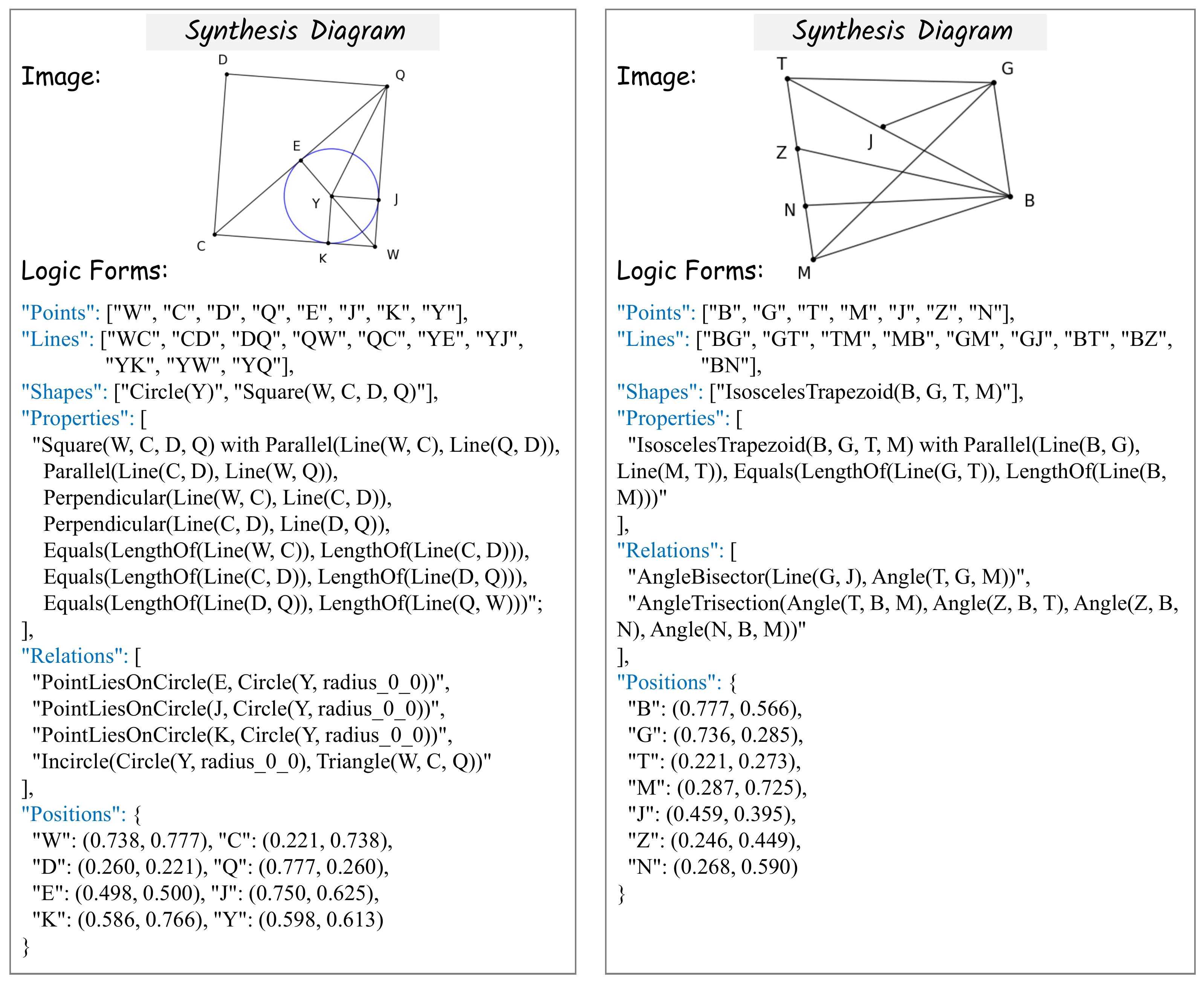
- Cost-Free Dataset Construction: A synthetic logic-form engine that constructs structured parsing paths (Point → Line → Shape → Shape Properties → Geometric Relations) paired with rendered diagrams, eliminating manual annotation.
- Rule-based Rewards: Computed via verifiable metrics such as F1 scores and L2 distances, removing hallucinated supervision.
- Hierarchical Dependency Modeling: Enforces step-level constraints (point-on-line, line-on-shape, shape-on-relation), ensuring geometric rewards are granted only when lower-level detections are reliable.
Symbolic Auto-Encoder
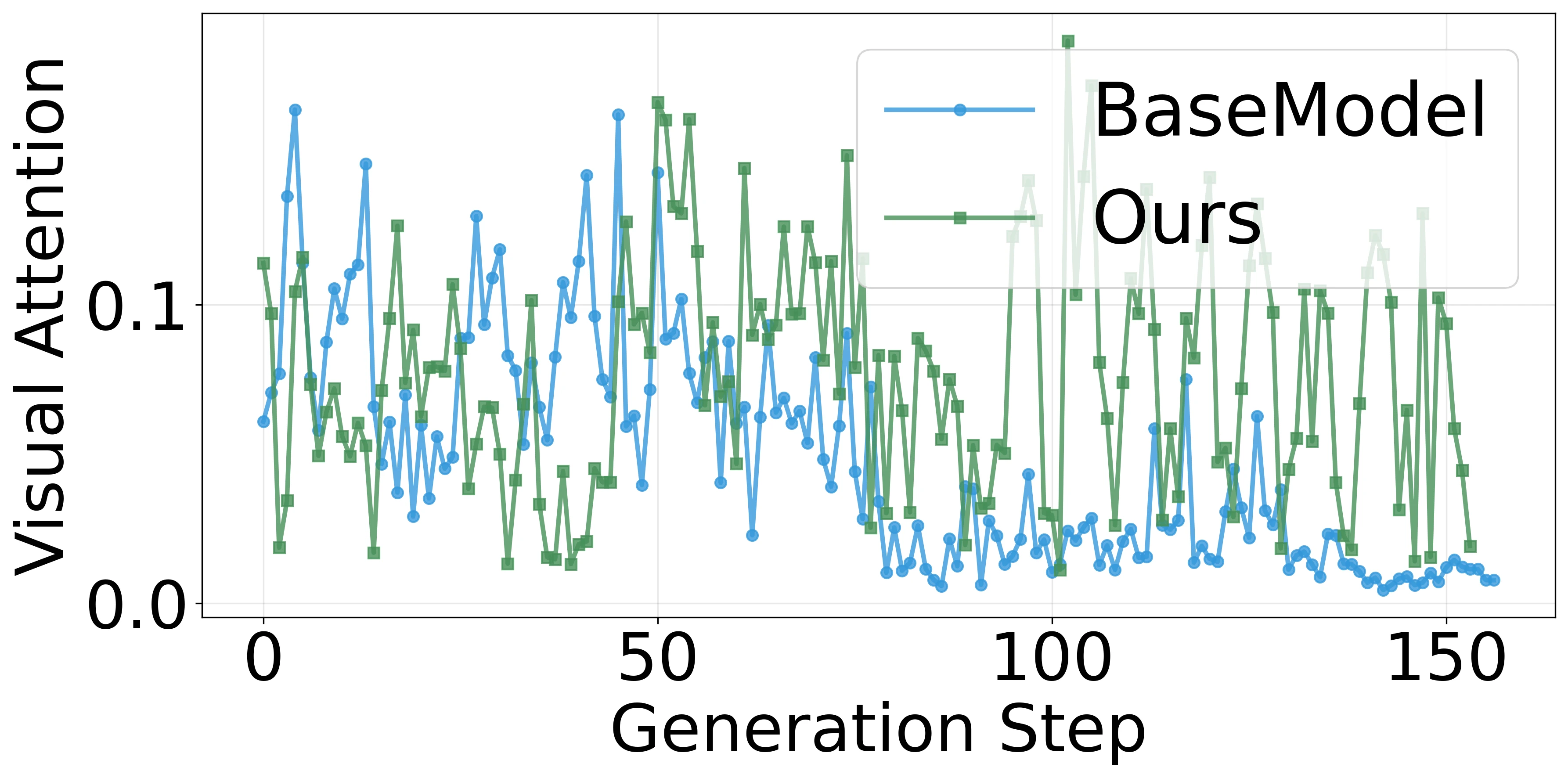
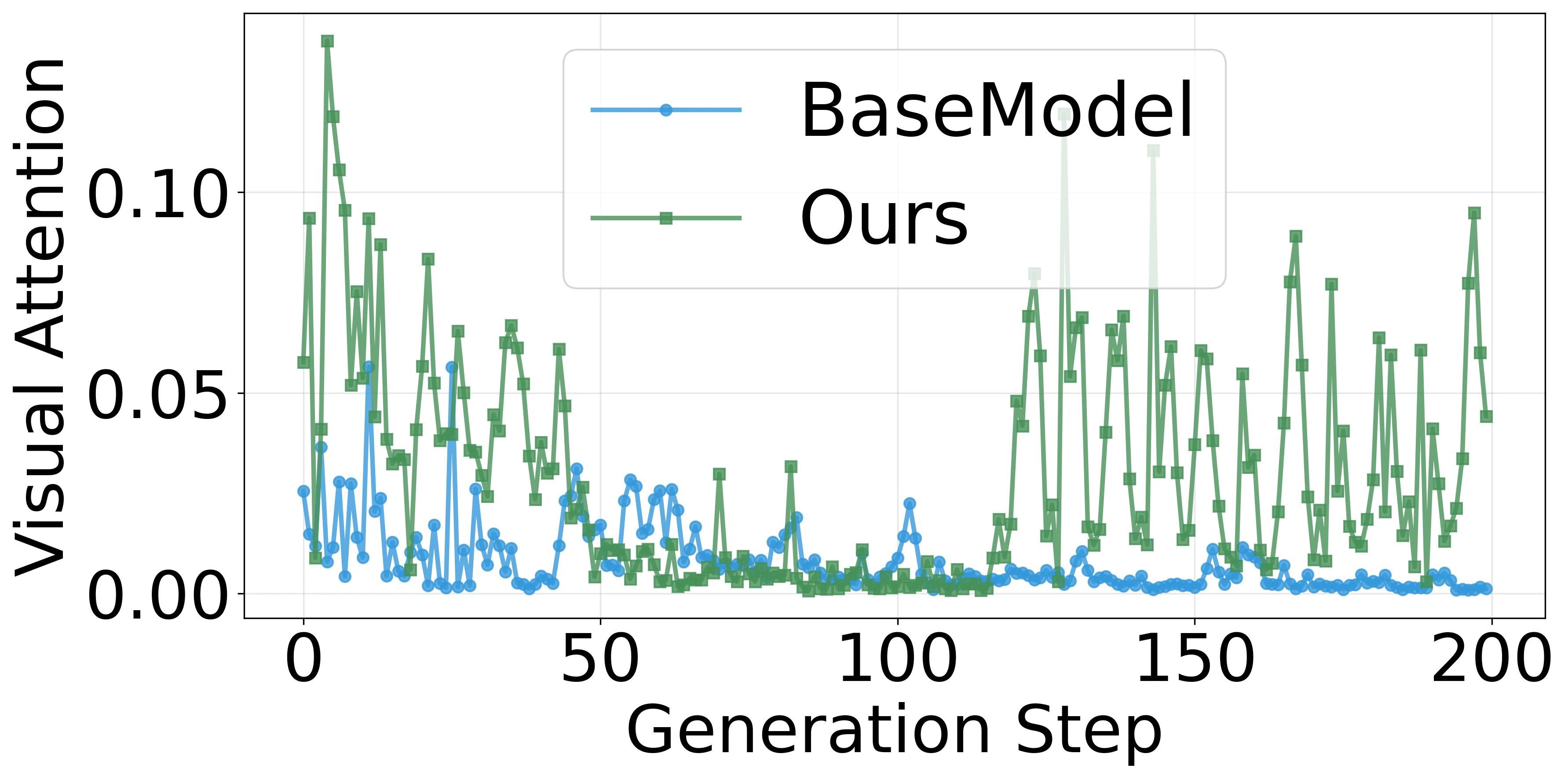
Our auto-encoder uses a rendering engine as decoder that reconstructs diagrams from symbolic logic forms. This enables self-supervised training through perceptual loss between input diagrams and their reconstructions. To address training collapse due to sparse supervision, we introduce two stabilization strategies:
- Hard Negative Contrastive Learning: Gaussian noise injection to increase reward variance.
- Power Normalization Annealing: Amplifies reward differences while preserving relative ranking.